async/await
什么是 async / await
async/await 是 ES8(ECMAScript 2017)引入的新语法,用来简化Promise异步操作。在async/await出现之前,开发者只能通过链式.then()的方式处理Promise异步操作。示例代码如下:
1 | import thenFs from 'then-fs' |
.then链式调用的优点:解决了回调地狱的问题
.then链式调用的缺点:代码冗余、阅读性差、不易理解
async / await 的基本使用
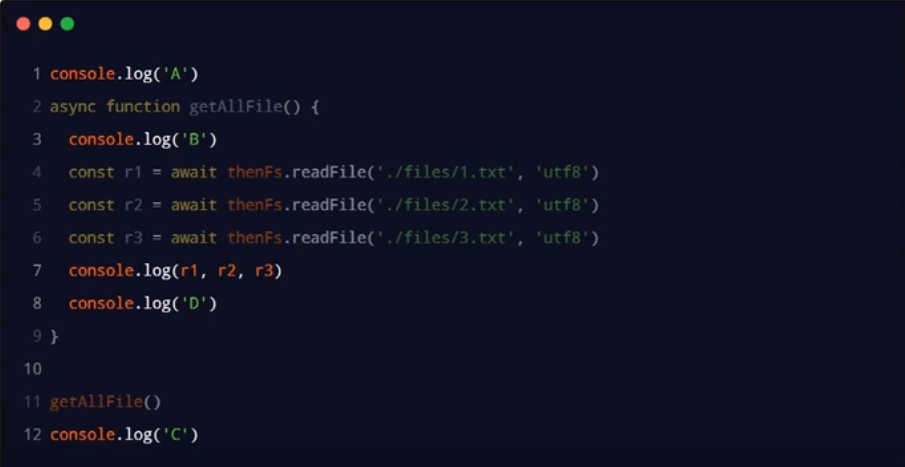
使用async/ await简化 Promise异步操作的示例代码如下:
1 | import thenFs from 'then-fs' |
如果某个方法的返回值是个Promise实例对象,那么我们就可以在前面用await来进行修饰,修饰完毕之后,这个返回值就不再是Promise实例,而是变成一个真正的值。
而且需要注意:如果这个方法内部用到了await,那么这个方法必须被async来修饰
注意事项
- 如果在 function 中使用了 await ,则 function 必须被 async 修饰
- 在 async 方法中,第一个 await 之前的代码会同步执行,await之后的代码会异步执行
最终输出的顺序:A、B、C、111 222 333、D
碰到第一个await,主线程就退出了方法执行,立马输出了C,当1 2 3异步读取完成之后就按顺序输出,最后异步的输出了D